Multinationality and cash holdings: Evidence from Japan
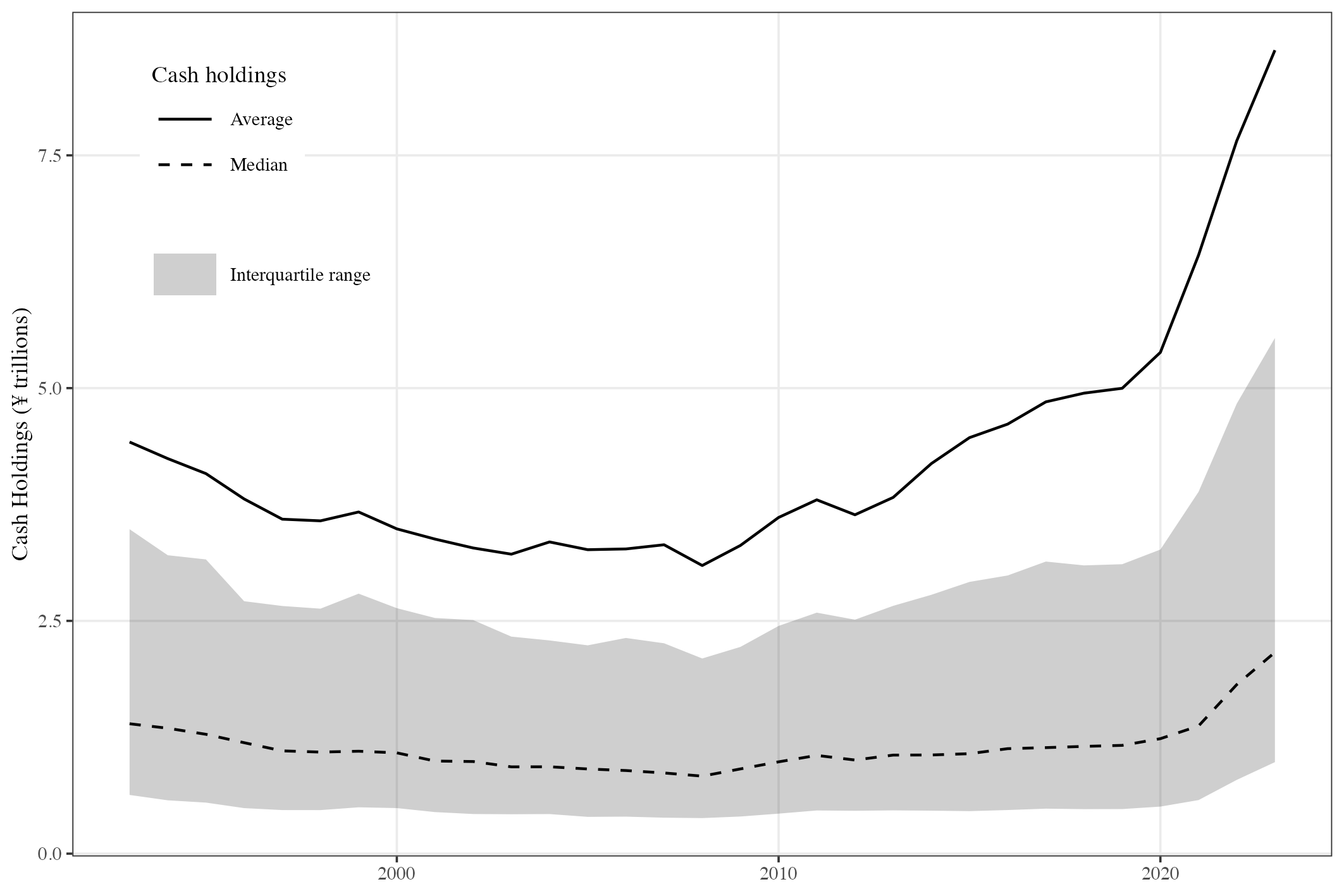
Abstract: Investors frequently criticise Japanese corporations for excessive cash holdings. On average and on aggregate, cash holdings have increased over the last decade. However, there is substantial variation in cash holdings within and between firms. At the same time, many large Japanese firms’ businesses have become more international. This research examines how international factors influence firms’ cash holdings via the precautionary motive – through overseas sales, foreign ownership, and cultural differences between the parent corporation and its overseas affiliates. Random effects within-between regression is used to jointly estimate the relationships within firms over time and between firms in the cross-section. Internationalisation through overseas sales has positive within and between firm relationships with cash holdings, but foreign shareholding is associated with lower cash holdings in the time series. Positive within-firm effects dominate the relationship between cash holdings and cultural heterogeneity.
Keywords: Cash holdings, Cultural heterogeneity, Foreign shareholding, Internationalisation, Japanese corporation, Multinationals, Overseas sales, Random effects within-between regression